[AI and copyright laws] Is your AI model's data usage compliant with copyright laws?
2023/02/14 | 3mins-
Haley (Content Communication)
This article was written based on educational materials from the Upstage AI Education & Content team.
-
THOSE WHO ARE DEALING WITH AI
ANYONE INTERESTED IN CREATING SERVICE-ORIENTED AI MODELS
THOSE WHO ARE CURIOUS ABOUT AI-RELATED COPYRIGHT LAWS
-
Are the mass learning necessary to create good AI models and the various data used for this are being used in compliance with copyright laws? Introducing the copyright laws you need to know to legally create AI-as-a-service models outside of an educational environment with assignments and data.
-
✔️ Copyright law, why do you need to know?
✔️ What is copyright law?
✔️ Lawful use of data
✔️ COPYRIGHT CASES THAT CAN OFTEN BE ENCOUNTERED WHILE WORKING ON AI
✔️ GRAY AREA OF COPYRIGHT LAW, AI
Recently, generative AI, such as ChatGPT and Midjourney, has become a hot topic every day, and interest in AI copyright is increasing. If so, are the various data we use when creating AI models are used in compliance with copyright laws?
This content introduces the copyright laws you need to know to legally create AI-as-a-service models outside of an educational environment where assignments and data are given . In particular, we will look at cases and questions that are commonly encountered in the process of creating data for AI models based on NLP (Natural Language Processing) technology.
Copyright law, why do you need to know?
GOOD AI MODELS COME FROM GOOD DATA.
When developing an AI model in an educational environment such as a school, you do not have to worry too much about this because teachers or curriculum administrators usually prepare data and tasks that do not have copyright problems. However, when it comes to actual work , in order to create a model that solves the problem I want to solve, I have to find and create appropriate data myself . If you think of this as simple and recklessly crawl data on the web and use it for model learning, you can violate copyright laws without knowing it. Therefore, we need to know about copyright laws before producing the data needed for AI model development.
Not only that, but academics are also paying attention to copyright and licensing. Since we are separately asking questions about whether the content of the thesis violates intellectual property rights or data collection methods, it is also necessary for those in the academic world to properly understand and utilize copyright.
Copyright, which is also attracting attention from the academic world (Source: International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing, ACL-IJCNLP 2021 )
IT IS NECESSARY TO PAY ATTENTION TO AMENDING THE LAW IN A GOOD DIRECTION CONSIDERING BOTH AI AND CREATORS.
A second reason to be concerned about copyright is that many copyright laws have not yet taken into account the development of AI models. It may seem paradoxical, but it is something that everyone needs to pay attention to for the positive development of AI. Mass learning is essential to create good AI, but there are no clear standards for copyright infringement when using data for AI training.
Looking at Article 1 (Purpose) of the Copyright Act, it is stated that “the purpose of this Act is to contribute to the improvement and development of culture and related industries by protecting the rights of authors and rights adjacent to them and promoting the fair use of copyrighted works.” . As you can see from reading this carefully , the current copyright law does not yet consider the “AI industry”. This is because at the time the law was enacted, AI did not receive as much attention as it does today, and its performance was not up to the current level.
FROM 2020, AN AMENDMENT TO THE COPYRIGHT ACT, WHICH INCLUDES A NEW COPYRIGHT DISCLAIMER IN THE AI FIELD, IS BEING PROMOTED TO REFLECT THIS CURRENT TREND, BUT CONTINUOUS ATTENTION IS NEEDED TO REVISE THE LAW IN A GOOD DIRECTION CONSIDERING BOTH AI AND CREATORS.
What is Copyright Law?
So what is copyright? Looking at the definition:
Copyright : The right given to creators for the results (works) that express people's thoughts or emotions. If there is “creativity,” it occurs naturally without a separate registration procedure.
(EXAMPLE: THE COPYRIGHT OF A PAINTING DRAWN BY ARTIST A NATURALLY BELONGS TO THE AUTHOR, A.)
If so, how does the law describe copyrighted works?
Work : The result of expressing a person's thoughts or feelings
Novels, poems, theses, lectures, speeches, screenplays, and other literary works
musical works
Drama, dance, pantomime and other theatrical works
Paintings, calligraphy, sculptures, prints, crafts, works of applied art and other works of art
Models and design books for buildings and construction, and other architectural works
Photographic works (including those produced in a similar way)
video work
Maps, charts, blueprints, schematics, models, and other graphic works
computer program work
There are many types of copyrighted works like this, and those who deal with AI will have heard a lot about text and image copyrighted works. Fields necessary for AI model development, such as literary, music, video, and photographic works, are also protected as copyrighted works.
However, there are works that are not protected by copyright law.
Works not protected by copyright law
Constitution, laws, treaties, orders, ordinances and rules
State or local government notices, announcements, instructions, and other similar matters
Judgment, decision, order, adjudication, administrative adjudication, and other resolutions and decisions of the court, etc.
Compilation or translation of the contents specified in subparagraphs 1 to 3 prepared by the state or local government
Reporting that is merely a statement of fact
This mainly applies to creative works written by the state or local governments, and includes current affairs reports that are difficult to be considered creative.
So, based on the contents so far, let's review the questions that may arise in real life about copyright.
[Case 1]
Q. I am trying to create and distribute a model that provides case precedent search service. Is it okay?A. Yes, it is possible. Since precedents are stipulated as copyrighted works not protected by the Copyright Act, making commercial services based on them or using them for research purposes does not violate the Copyright Act.
[Case 2]
Q. I was so impressed with Upstage blog content that I left a comment. Do I own the copyright of this comment?A. It depends on the content of the comment. “It was so good!” If it is a sentence that can be written universally by anyone, it is not protected by copyright, but a sentence at a level where “creativity” is recognized is copyrighted.
For example, in the case of a very short six-word novel written by Hemingway, Hemingway owns the copyright because creativity is recognized.
IF SO, COPYRIGHT NATURALLY OCCURS FOR WORKS WHOSE CREATIVITY IS RECOGNIZED, SO LET'S TAKE A CLOSER LOOK AT HOW TO PROPERLY USE DATA FOR AI MODEL LEARNING.
How to use your data legally
1. Consultation with the author
This is a method of negotiating directly with the copyright holder and discussing the method of use. Usually, if you look at the homepage, there is a contact or e-mail address where you can negotiate about the copyrighted work, and you can negotiate through it. There are various ways to negotiate the use method. According to the contents of the contract specified by the Korea Copyright Commission, there are measures such as obtaining permission to use copyrighted works or acquiring copyrighted property rights .
Let's interpret the meaning of the above plan as follows.
(1) Exclusive / non-exclusive license for copyright
Exclusive license: The author gives permission to exercise the “exclusive” right to the use of data to the user who has entered into a contract
Non-exclusive license: Authors may enter into data usage agreements in addition to contracted users
(2) Transfer of all/part of author's property rights
It is the right to transfer all or part of a naturally occurring copyright. All or part of the copyright can be acquired, and it is also possible to take over for a certain period of time.
If so, is there any other way other than making a contract and using it? There is an efficient method for both authors and users, and “license” plays that role.
2. License
The second way to legally use data is through the terms of use stated by the author, or 'license'. A license is a stipulation that allows users to use a work if certain conditions suggested by the author are met, even if the author is not asked for permission to use it.
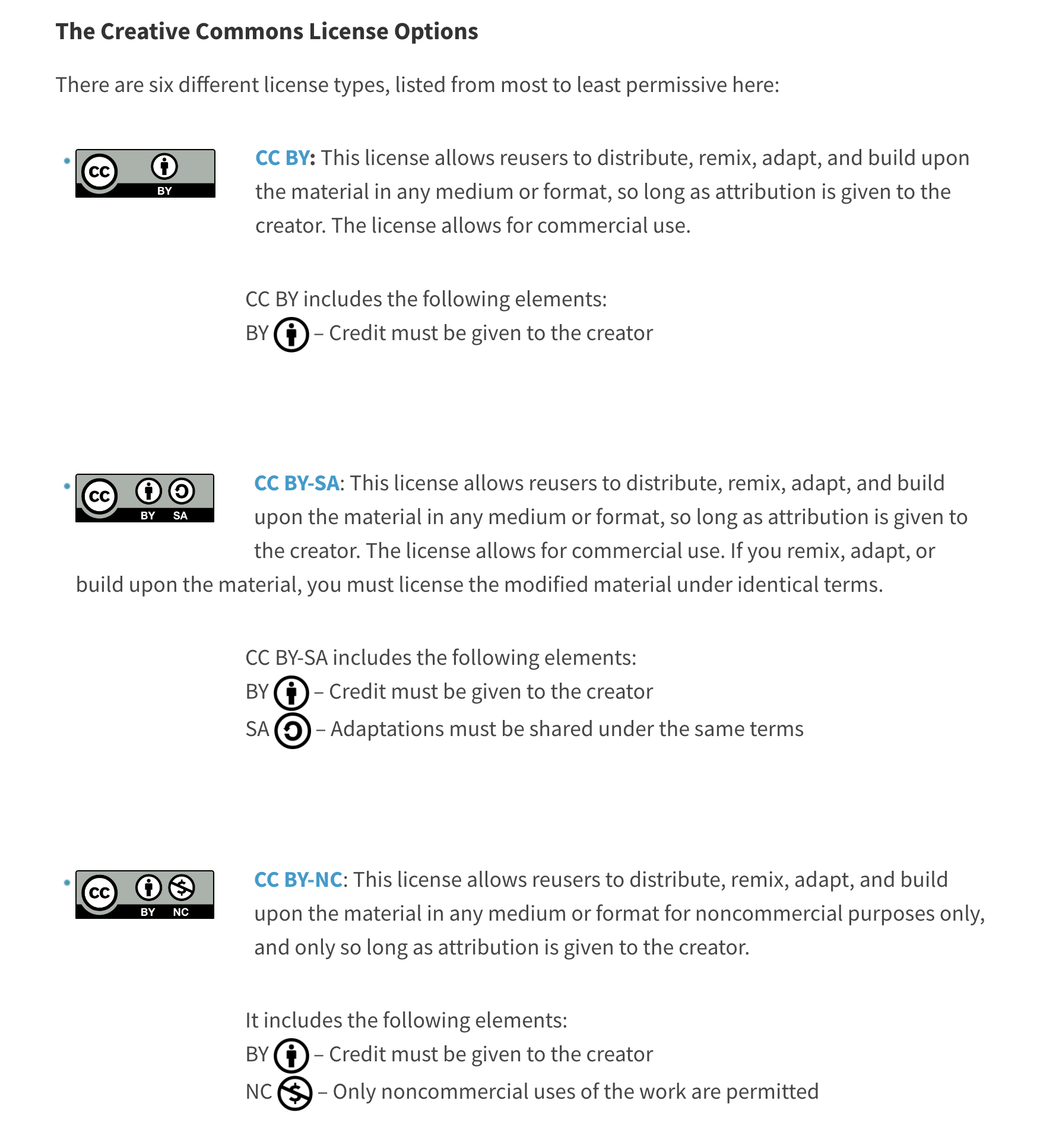
There can be a variety of organizations that issue licenses, but the most famous among them is 'CCL' provided by a non-profit organization called Creative Commons, and based on this, there is 'Gonggongnuri' provided by the Ministry of Culture, Sports and Tourism in Korea.
MEANING OF CCL
BY: Attribution
ND: NoDerivatives
NC: Non-Commercial
SA: ShareAlike
CCL widely used internationally (Source: Creative Commons homepage)
A typical example of CC-BY-NC-SA is ' Namu Wiki '. If you want to use Namuwiki data for AI model development, you can use it under the following conditions.
[Case 3]
Q. Is it possible to create a MRC (Machine Reading Comprehension, a technology in which AI algorithms analyze problems and find optimal answers to questions) datasets by crawling Namuwiki data, and then distribute them through personal Github?A. YES, AS LONG AS IT IS PART OF A SCHOOL, AS IT IS CONSIDERED NON-PROFIT. HOWEVER, EVEN IF YOU DISTRIBUTE IT, YOU MUST ATTACH CC-BY-NC-SA, THE LICENSE OF THE ORIGINAL DATA, AND THE SOURCE OF THE ORIGINAL DATA MUST BE SPECIFIED.
As another example, let's take a look at CC-BY-ND. This is a license that combines BY, which means attribution, and ND, which means no change. As a representative example of this, a dataset called ' KorQuAD ' , which is well known to those who do Korean NLP, is distributed under this license.
[Case 4]
Q. After creating a new MRC dataset by changing only KorQuAD's questions, can I distribute it to my personal GitHub?A. It is not possible to change and disclose KorQuAD's fingerprints, questions, and answer pairs due to the prohibition of change.
WHAT OTHER COPYRIGHT-RELATED CASES CAN YOU OFTEN ENCOUNTER WHILE DEVELOPING AI MODELS?
COPYRIGHT CASES THAT CAN OFTEN BE ENCOUNTERED WHILE WORKING ON AI
Use of news data
First of all, news data is a common example when developing AI models. However, you should be aware of the fact that the copyright of news articles belongs to the media .
Examples of copyright notation by domestic media companies
Currently, the Korea Press Foundation consigns and manages the copyrights of most media companies. Therefore, in order to legally use a news article, if the media company providing the article has entrusted the copyright to the Korea Press Promotion Foundation, you must contact the foundation, otherwise you must directly inquire with the media company about the scope of content use and terms of the contract. It is good to note that major media outlets often manage their copyrights without entrusting them to the Korea Press Foundation. Or, in very rare cases, there are media outlets (ex. Wikitree) where CCL is applied, so it is important to check this according to the purpose of use.
SOMETIMES KDX (KOREA DATA EXCHANGE) PUBLISHES NEWS DATA FOR FREE. AT THIS POINT, YOU MAY BE WONDERING HOW FAR YOU CAN USE THIS DATA.
[Case 5]
Q. Can I use the data I purchased for 0 won?
A. In this case, it depends on the terms and conditions set by the data seller.
SOURCE: KDX KOREA DATA EXCHANGE
BASICALLY, KDX CAN BE USED ONLY WITHIN THE SCOPE OF COMMON USE IN ARTICLES A, B, AND C BELOW, AND IF THE SELLING MEMBER HAS ADDITIONAL CONDITIONS, OTHER USES OUTSIDE THE COMMON SCOPE OF USE MAY NOT BE POSSIBLE, SO YOU SHOULD TAKE A CLOSER LOOK.
Source: KDX Korea Data Exchange
title of news article
On the other hand, surprisingly, the title of a news article is not protected by copyright law because it is not recognized for its value as a copyrighted work. This is also stated in the booklet “Newspapers and Copyright” issued by the Korea Copyright Commission.
Source: Newspaper and Copyright, Korea Copyright Commission, 2009
So if you want to build a model that predicts which category a news article belongs to just by looking at the headline, you can legitimately use that data.
Fair-use
In the following cases, you can use the copyrighted work without obtaining permission from the copyright holder. Usually, for educational purposes, it is within these fair use purposes, so there is no restriction on the copyrighted work.
education , etc.
Duplication in court proceedings, etc.
use of political speeches, etc.
Use for school educational purposes, etc.
Use for current affairs reporting
Use of published works
Non-profit performance/broadcasting
Reproduction for private use
Reproduction in libraries, etc.
Replication as a test question
Reproduction for the blind, etc.
Temporary recording and recording of broadcasters
Exhibition or reproduction of works of art, photography or architecture
Use by translation, etc.
Reproduction of topical articles and editorials
Reverse program code analysis
Reproduction of programs for preservation by legitimate users
-Source: Korea Copyright Commission
THE GRAY AREA OF COPYRIGHT LAW, AI
It seems that many parts are regulated in the copyright law , but the copyright law related to AI still has a long way to go. Can the data generated by ChatGPT, which has recently become a hot topic, be recognized as copyrighted work? If this is possible, we still have to solve, such as what license should be attached to the data generated by ChatGPT, how far it can be used, and what will happen to the copyright of the AI model that produces new results based on news articles. There are many parts.
Therefore, until clear relevant standards are established, first of all, it is necessary to check the copyright and license of the work, and carefully examine the scope of use . In this content, we mainly looked at CCL licenses, but there are many other types of licenses, so it is necessary to take a look before using data.
I HOPE THAT EVERYONE WORKING WITH AI UNDERSTANDS HOW DATA IS CREATED WITHIN LEGAL BOUNDARIES, SO THAT AI MODELS CAN BE DEVELOPED IN A BETTER DIRECTION, AND THAT IT WILL ALSO BE AN OPPORTUNITY TO PAY ATTENTION TO THE LIMITATIONS OF CURRENT COPYRIGHT LAWS.
-
-
Upstage, founded in October 2020, offers a no-code/low-code solution called "Upstage AI Pack" to help clients innovate in AI. This solution applies the latest AI technologies to various industries in a customized manner. Upstage AI Pack includes OCR technology that extracts desired information from images, recommendation technology that considers customer information and product/service features, and natural language processing search technology that enables meaning-based search. By using the Upstage AI Pack, companies can easily utilize data processing, AI modeling, and metric management. They can also receive support for continuous updates, allowing them to use the latest AI technologies conveniently. Additionally, Upstage offers practical, AI-experienced training and a strong foundation in AI through an education content business. This helps cultivate differentiated professionals who can immediately contribute to AI business.
Led by top talents from global tech giants like Google, Apple, Amazon, Nvidia, Meta, and Naver, Upstage has established itself as a unique AI technology leader. The company has presented excellent papers at world-renowned AI conferences, such as NeurIPS, ICLR, CVPR, ECCV, WWW, CHI, and WSDM. In addition, Upstage is the only Korean company to have won double-digit gold medals in Kaggle competitions. CEO Sung Kim, an associate professor at Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, is a world-class AI guru who has received the ACM Sigsoft Distinguished Paper Award four times for his research on bug prediction and automatic source code generation. He is also well-known as a lecturer for "Deep Learning for Everyone," which has recorded over 7 million views on YouTube. Co-founders include CTO Hwal-suk Lee, who led Naver's Visual AI/OCR and achieved global success, and CSO Eun-jeong Park, who led the modelling of the world's best translation tool, Papago.